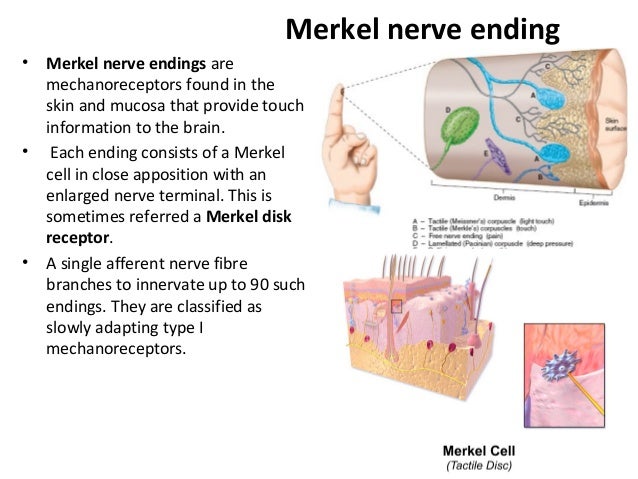
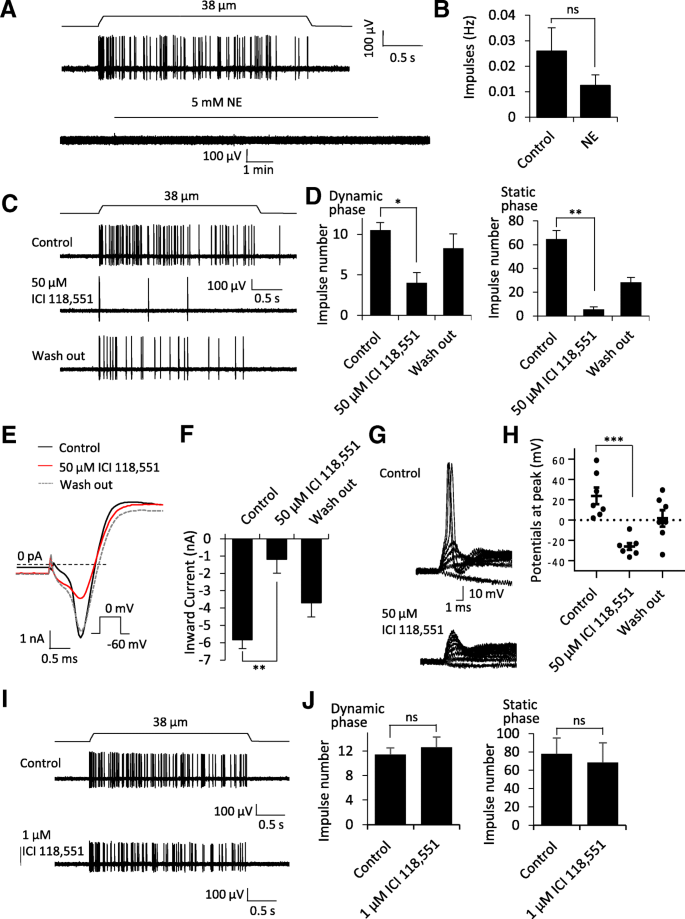
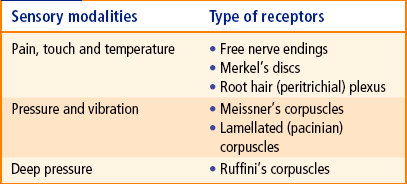
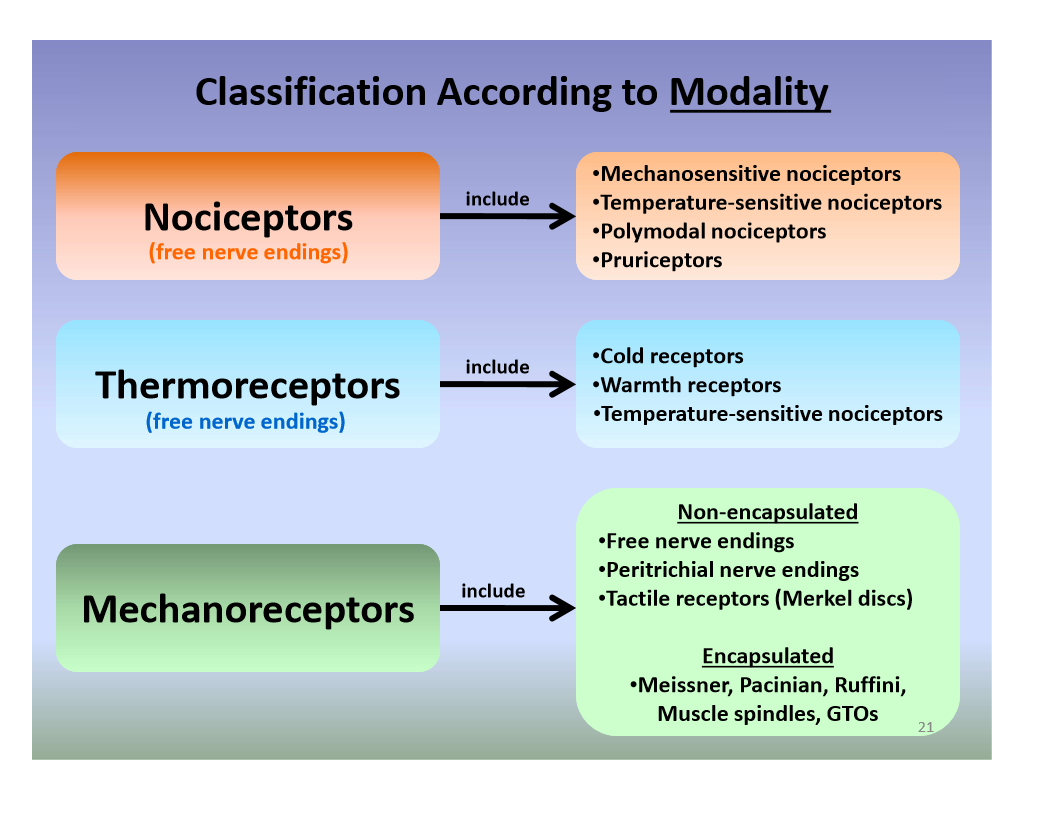
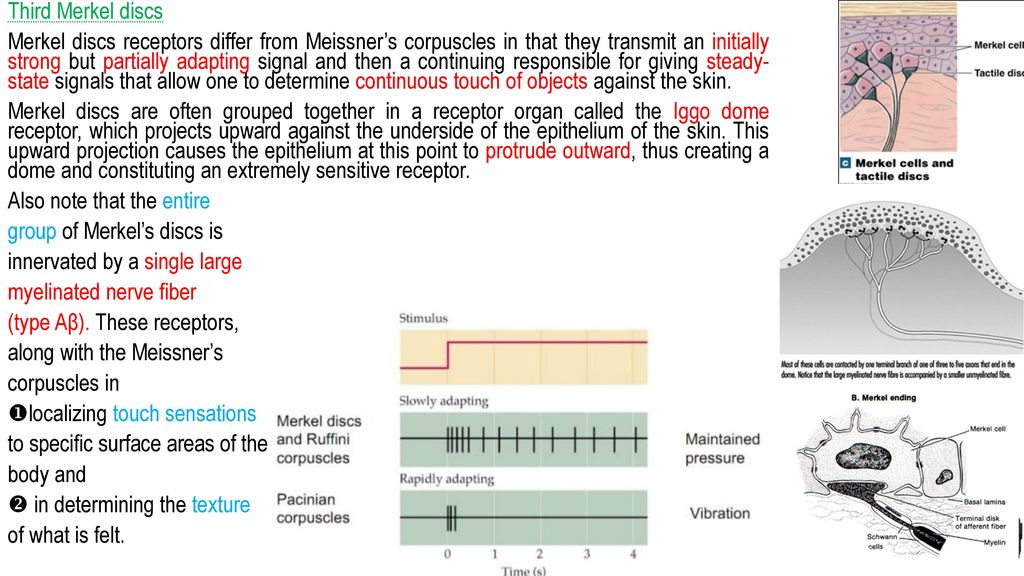
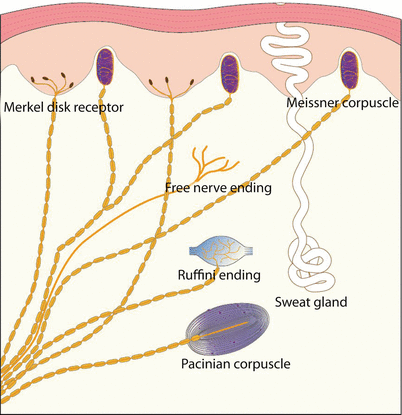
Merkel Discs Receptor
When the sensation of light touch is detected the merkel cell neurite complex acts as what is called a mechanoreceptor.

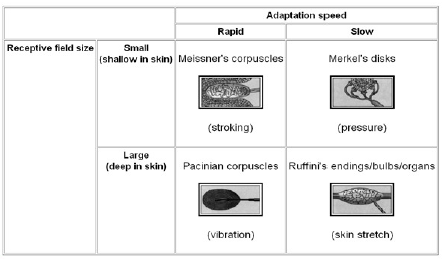
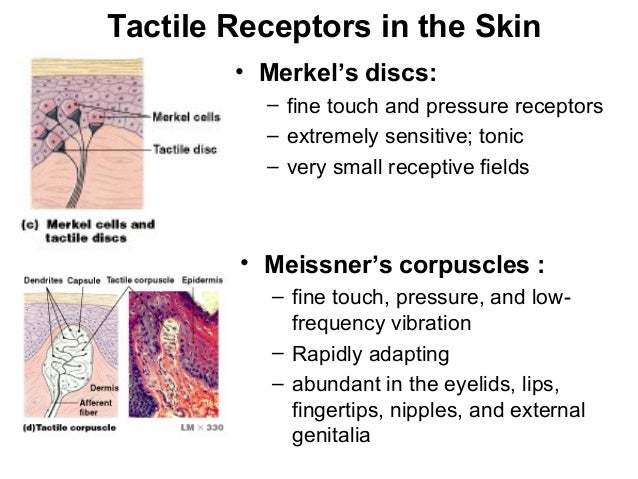
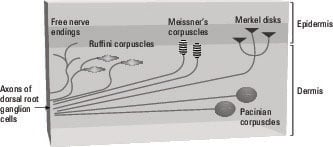
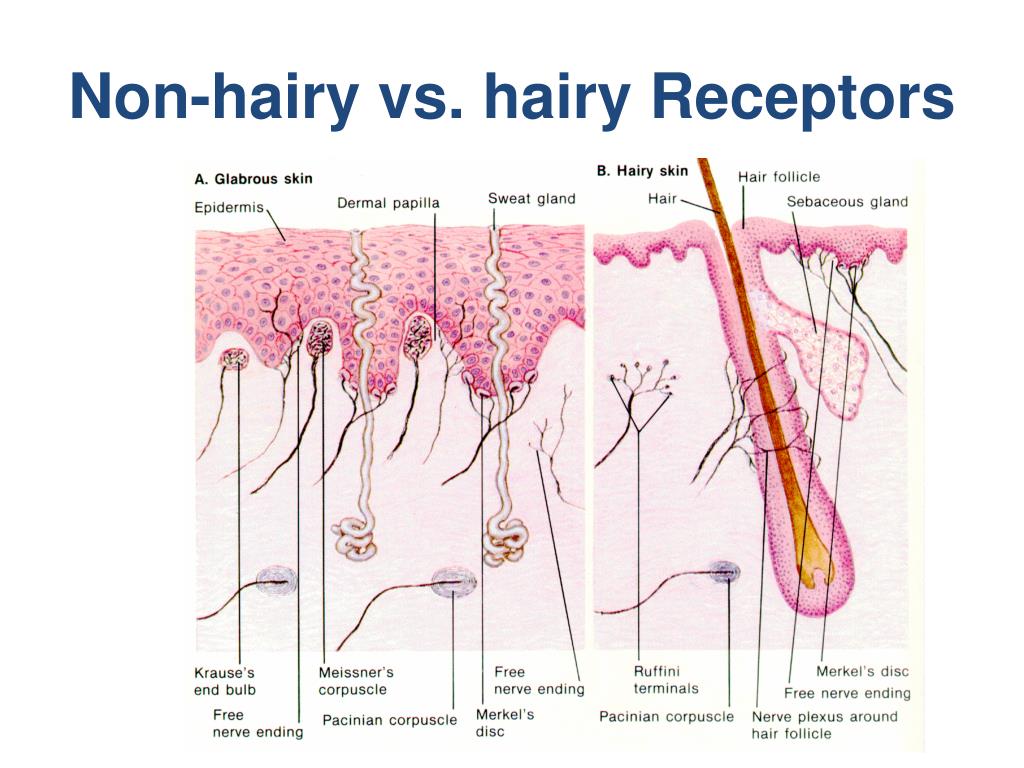
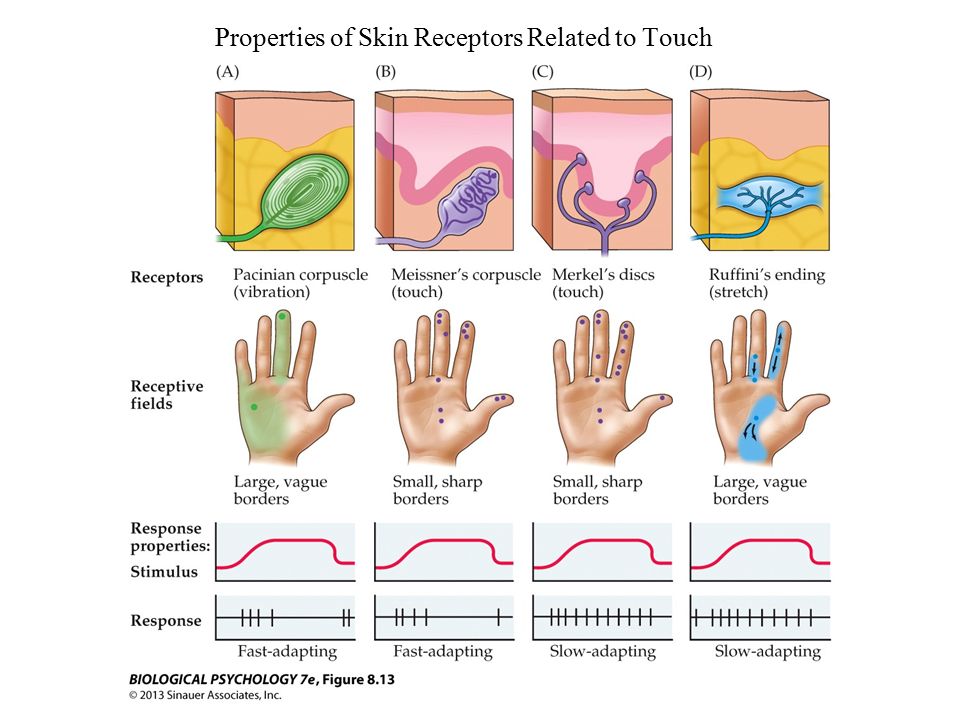
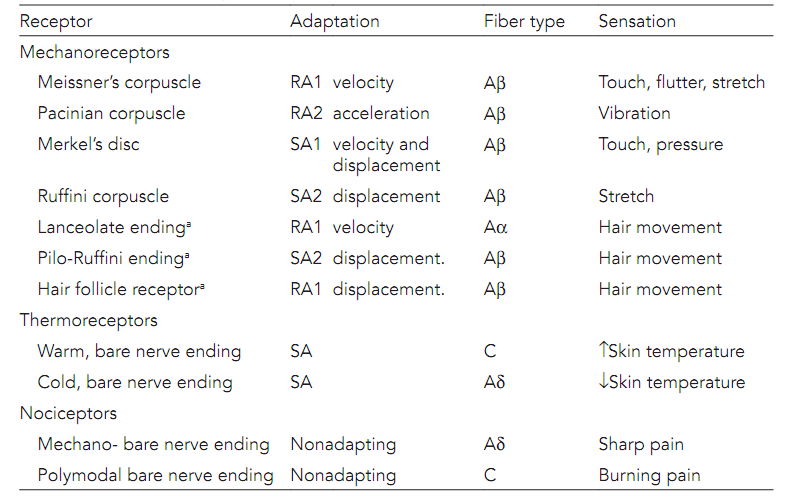
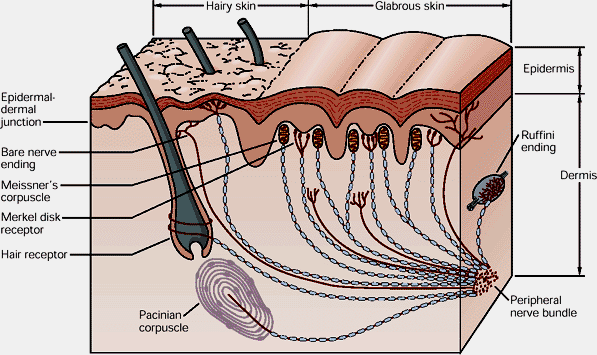
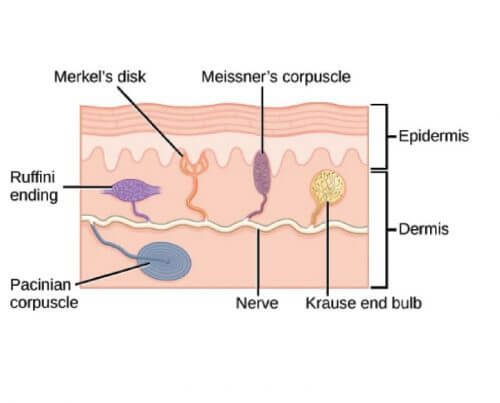
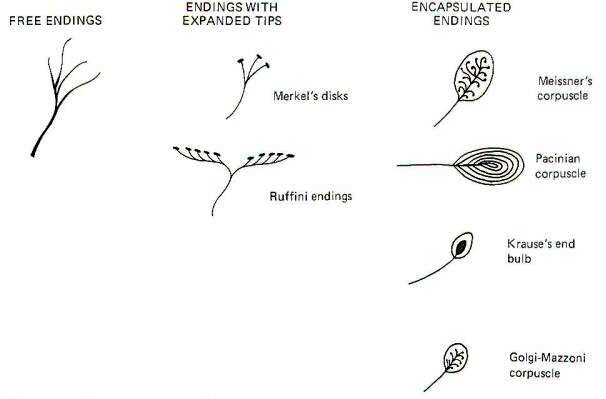
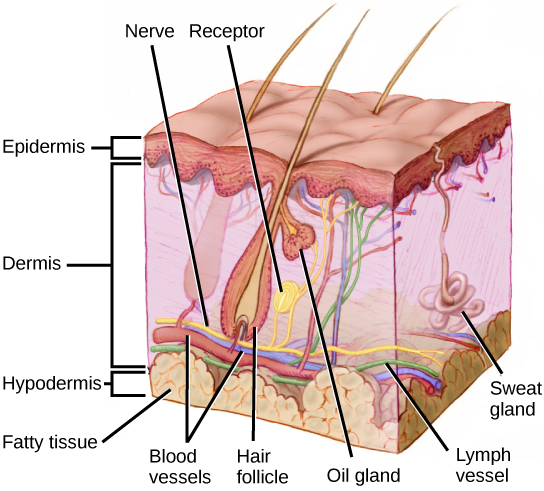
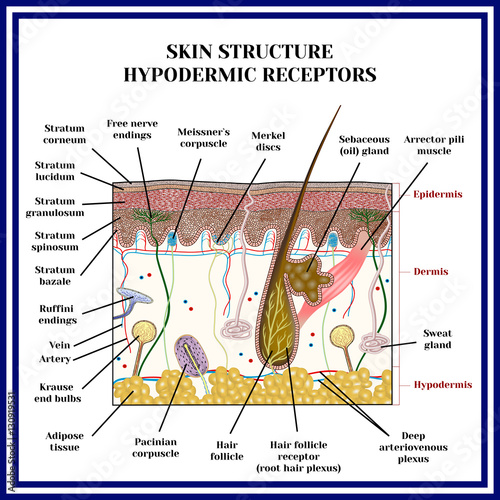
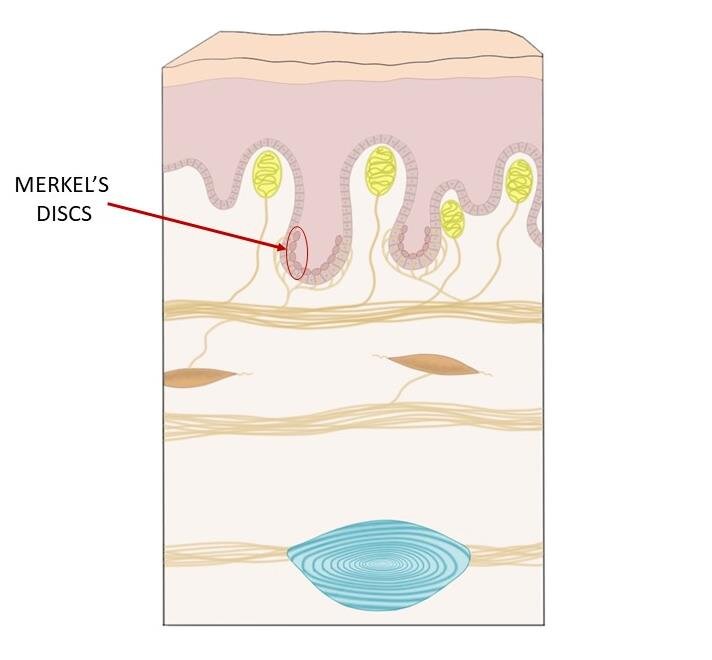
Merkel discs receptor. They are nerve endings and provide information on mechanical pressure position and deep static touch features such as shapes and edges. Merkel nerve endings are mechanoreceptors a type of sensory receptor that are found in the basal epidermis and hair follicles. Each ending consists of a merkel cell in close apposition with an enlarged nerve terminal. Merkels disks are located superficially in the dermis of skin at the base of the epidermis and lie adjacent to meissners corpuscles and sweat glands.
Merkel cells also known as merkel ranvier cells or tactile epithelial cells are oval shaped mechanoreceptors essential for light touch sensation and found in the skin of vertebrates. Though it has been reported that merkel cells are derived from neural crest cells more recent experiments in mammals have indicated that they are in fact epithelia. Merkel cells in the basal epidermis of the skin store serotonin which they release to associated nerve endings in response to pressure. They adapt slowly to pressure and therefore record the sustained presence of pressure on the skin.
In the skin merkel receptor cells are typically situated near sensory nerve endings with each merkel cell and each nerve ending forming what is known as a merkel cell neurite complex. Merkel cells register gentle touch. These receptors respond to indentation of the skin.









:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/3467/gScufXXNtljr9Y0BBXdtw_Ruffini_s_corpuscle.png)
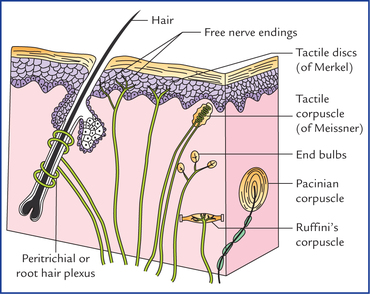
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/article/en/peripheral-mechanosensory-receptors/fnl8DI8PJ2YdW6Em8Z2m7g_tf1Nh3joMOYUYb44sj8KBQ_Dendrites.png)

























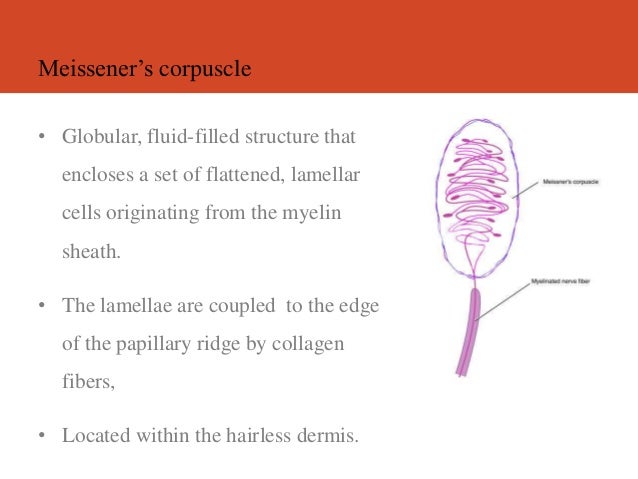
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/3470/7UckPYLm3F5EmutWIQmlQ_Meissner_Corpuscle.png)