Merkel Disc Function
The merkel disc is a main type of tactile end organ for sensing gentle touch and is essential for sophisticated sensory tasks including social interaction environmental exploration and tactile discrimination.

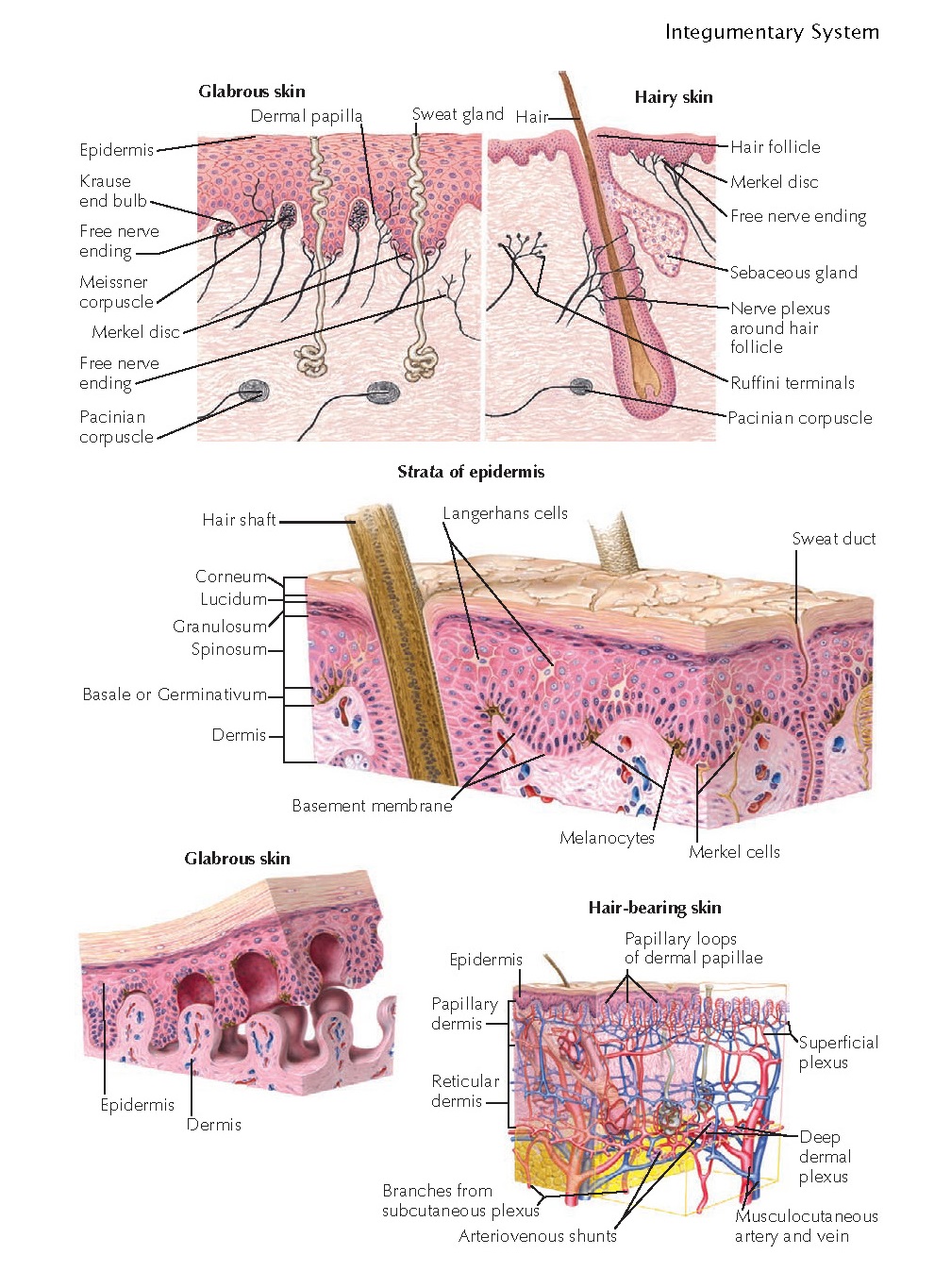
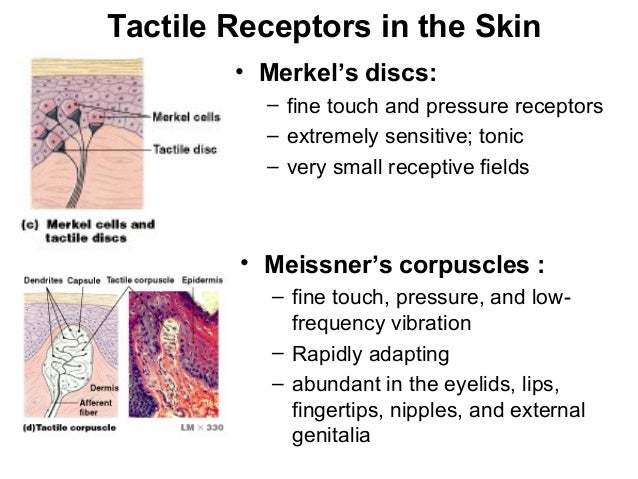
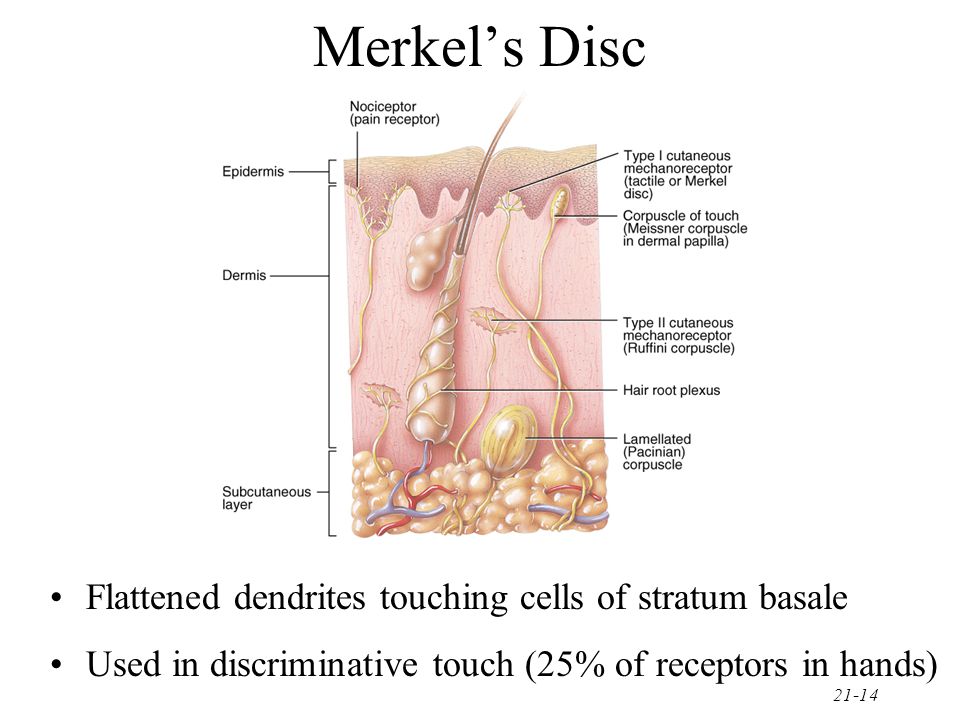
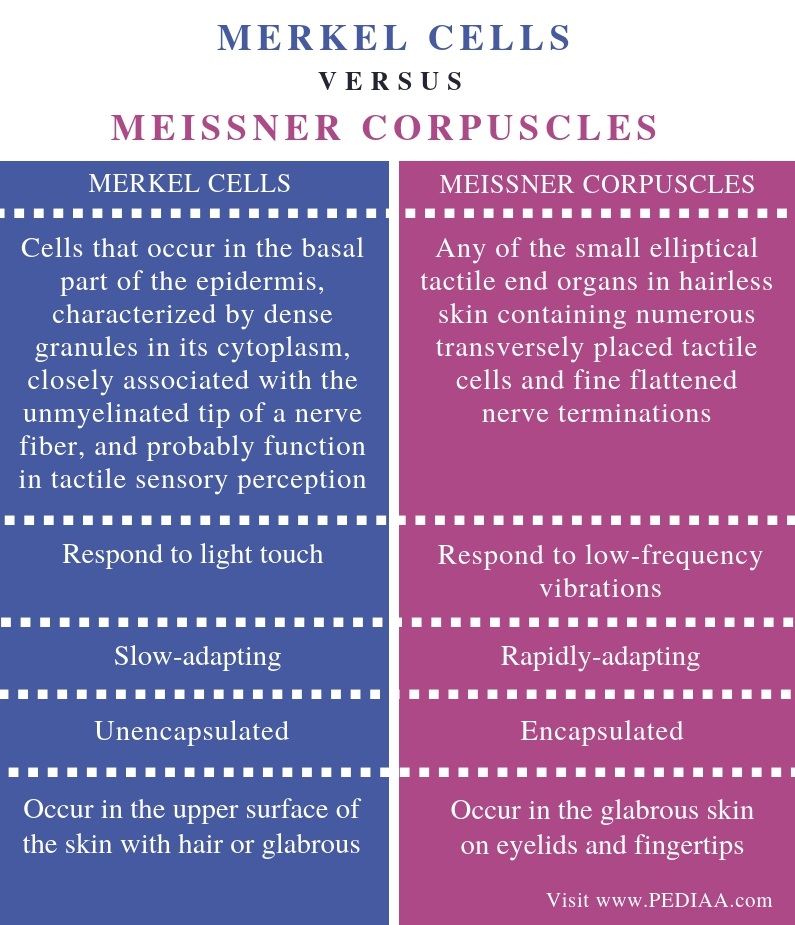
Merkel disc function. Merkels disk are slow adapting unencapsulated nerve endings that respond to light touch. Electrospun materials for tissue engineering and biomedical applications 2017. And with merkels disk this is just a specialized keratinocyte or an epithelial cell. They are present in the upper layers of skin that has hair or is glabrous.
They are present in the upper layers of skin that has hair or is glabrous. The german anatomist friedrich sigmund merkel referred to these cells as tastzellen or touch cells but this proposed function has been controversial as it has been hard to prove. Embryonic disk germ disk germinal. Often spelled disc in names of anatomic structures.
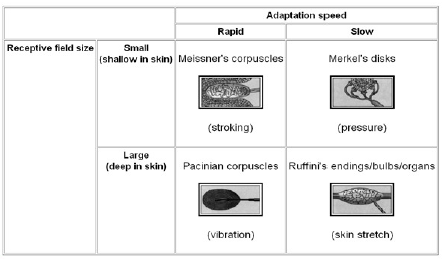
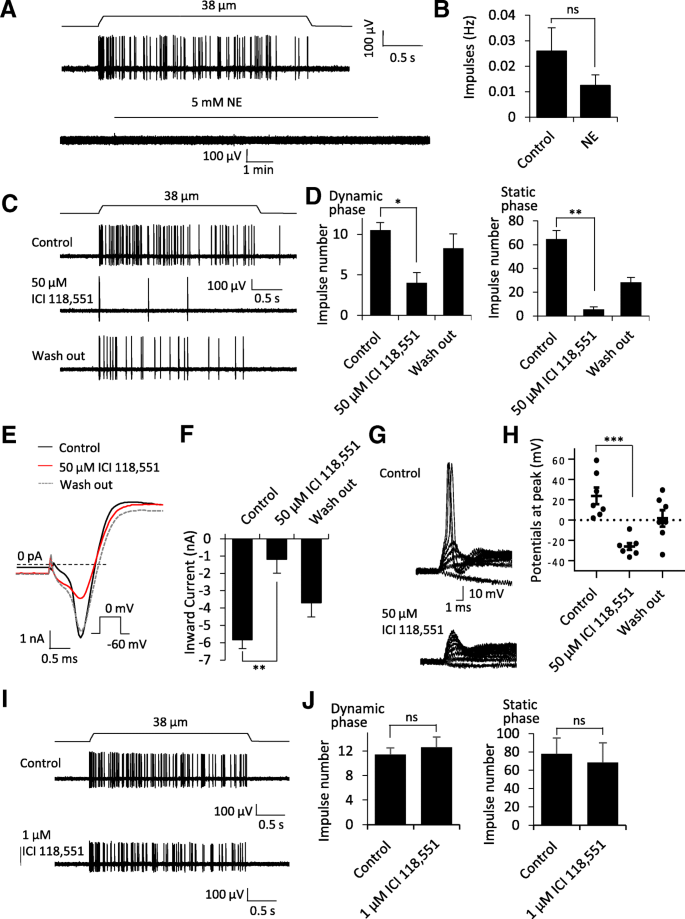
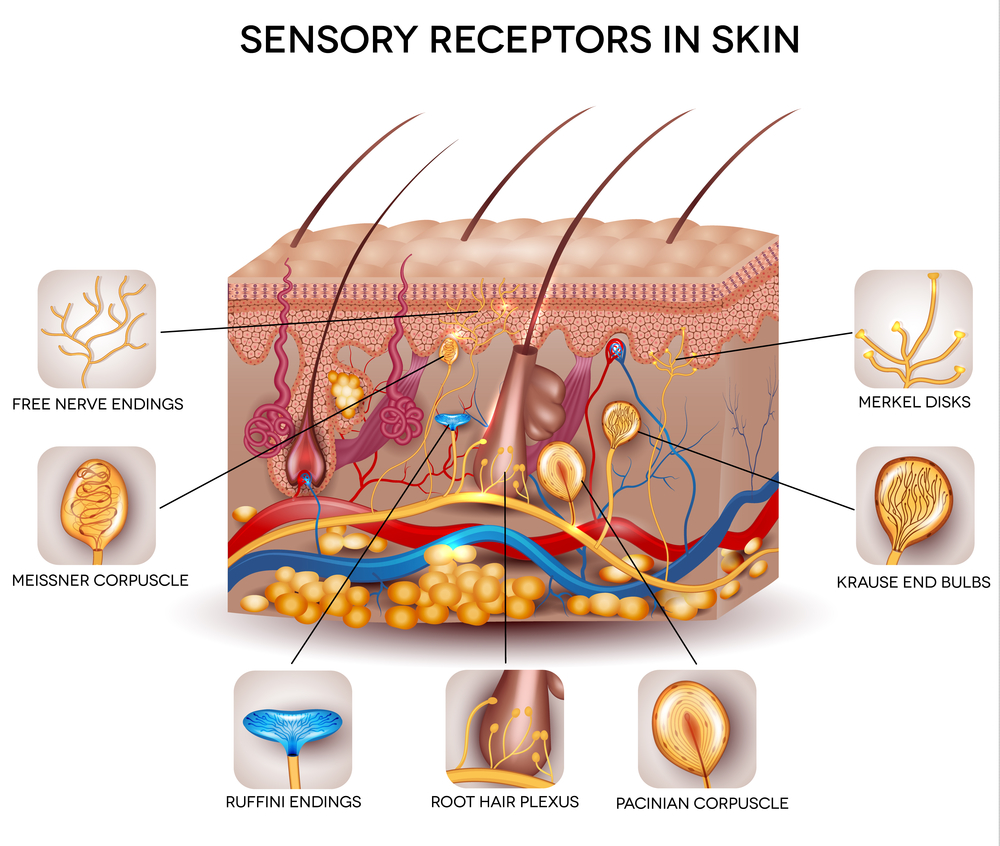
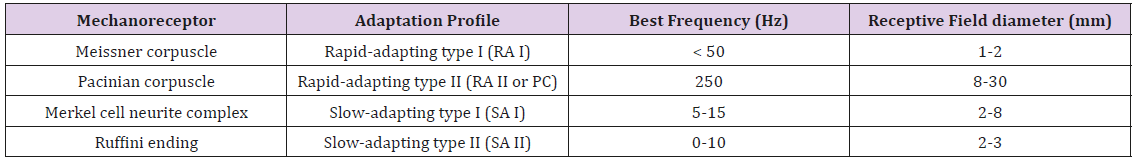
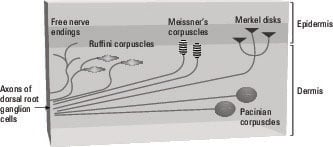
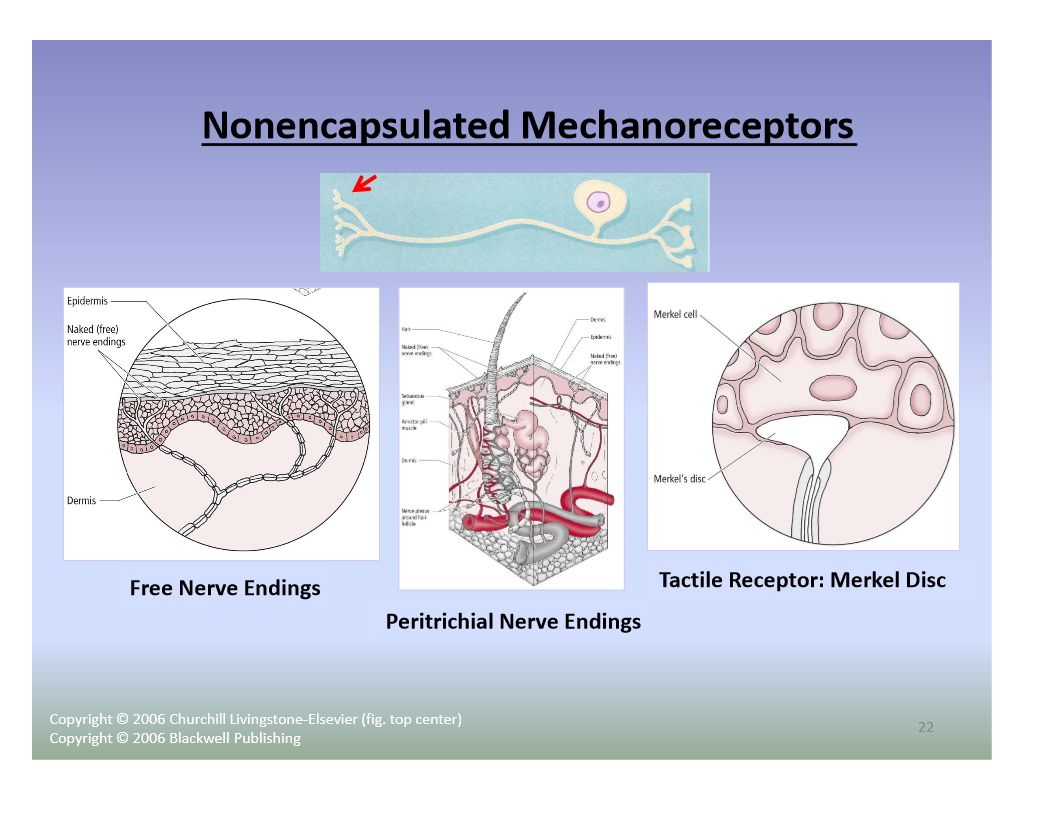
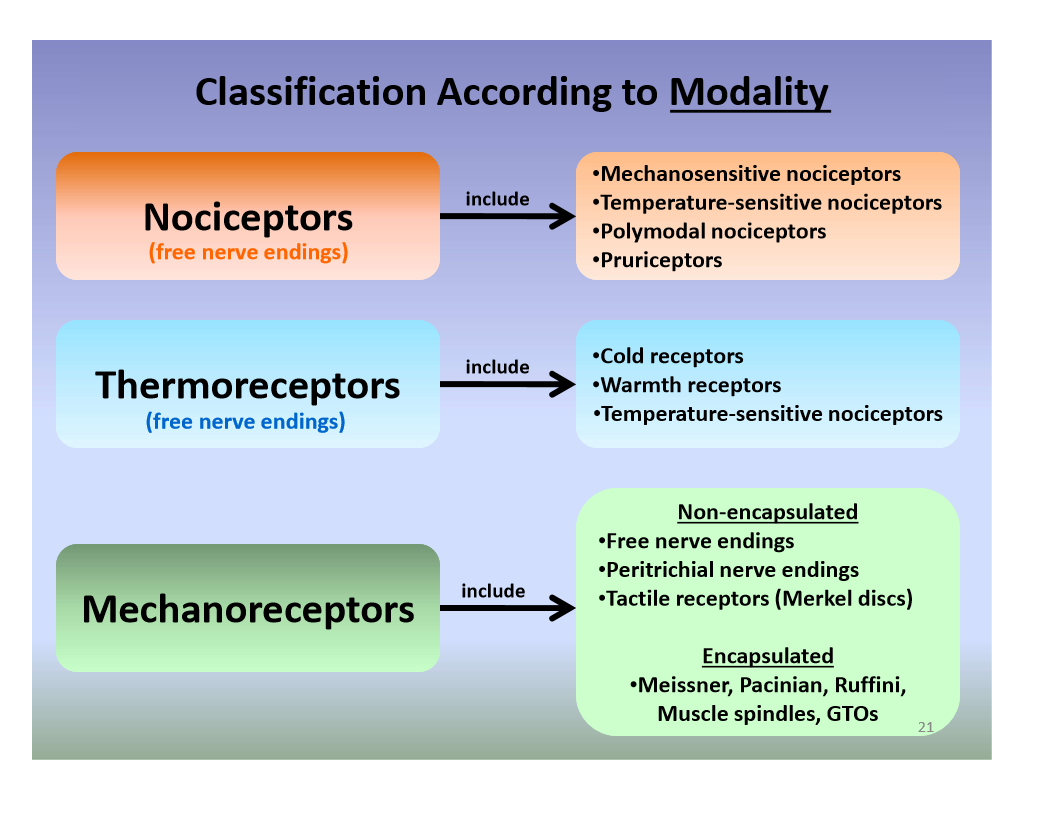
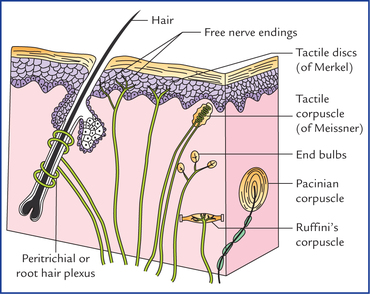
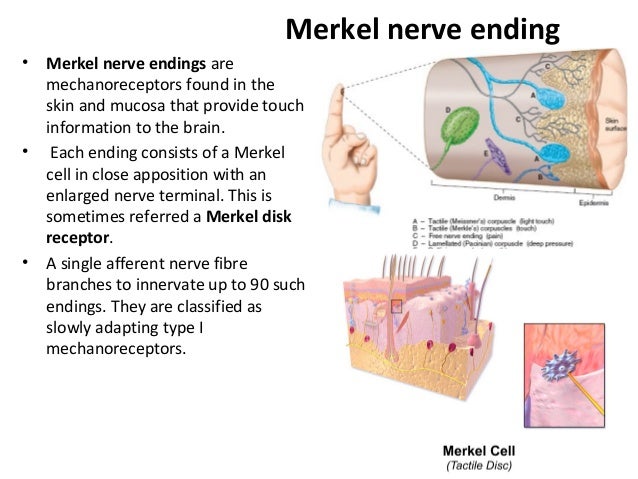
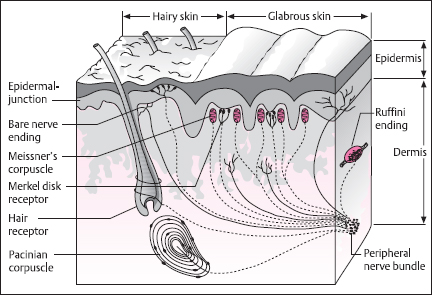
The four major types of tactile mechanoreceptors include. Ion channels will open that allow sodium to enter merkels disk. Though genetic knockout mice have recently shown that merkel cells are essential for the specialized coding by which afferent nerves resolve fine spatial details. Each ending consists of a merkel cell in close apposition with an enlarged nerve terminal.
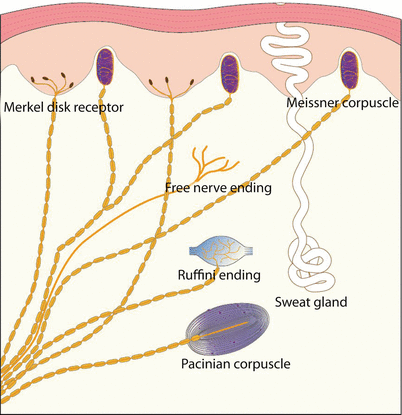
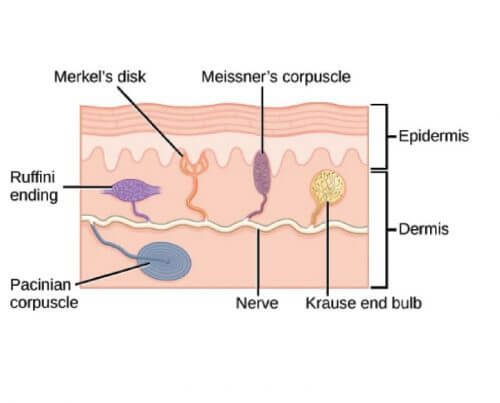
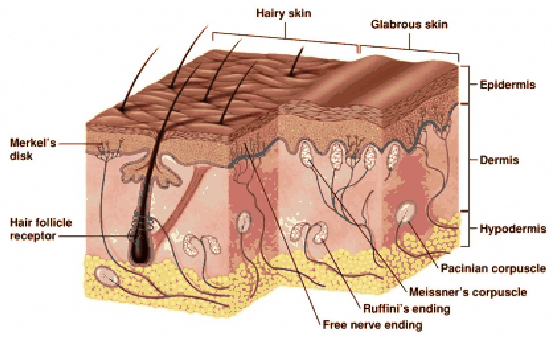
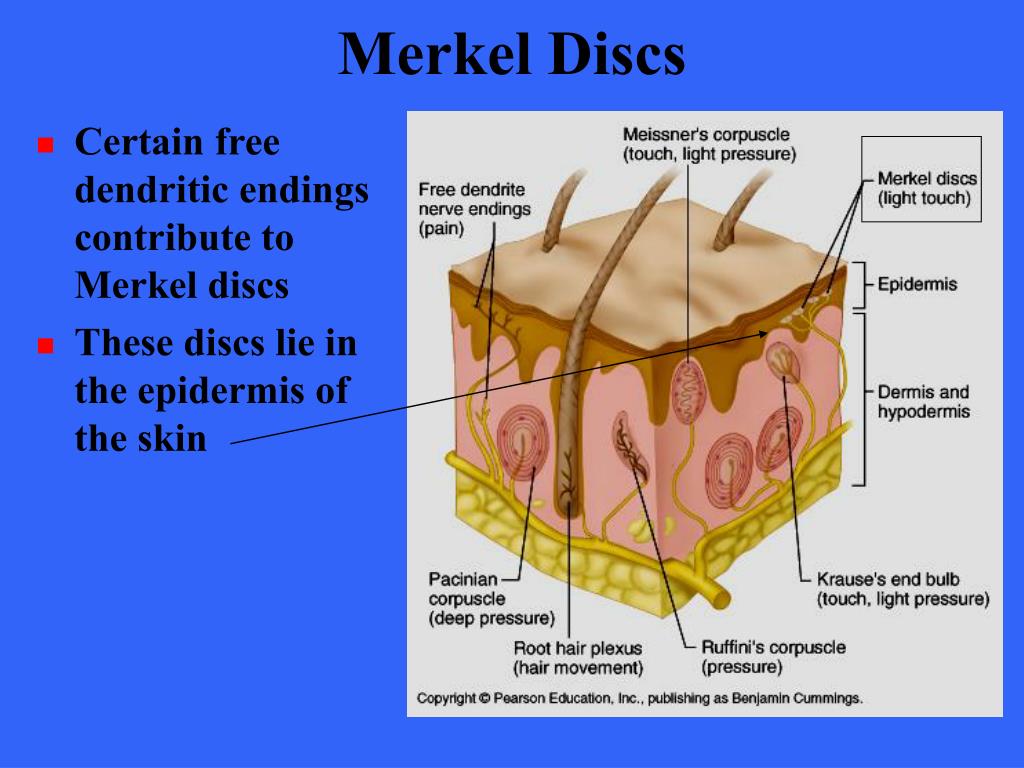
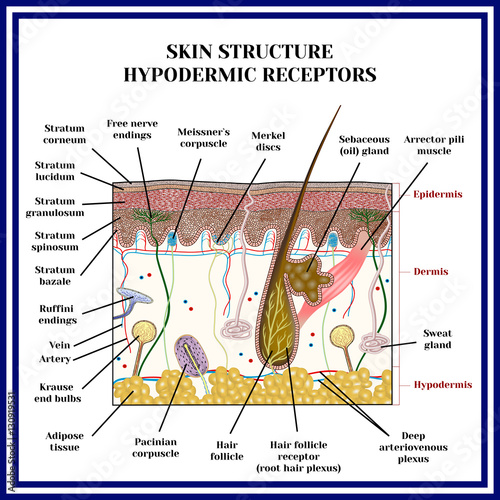
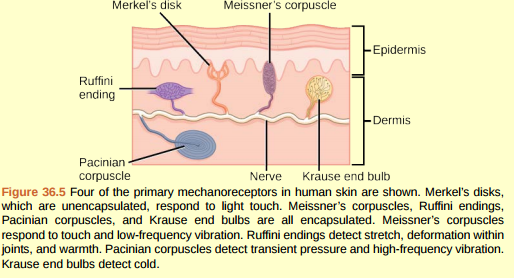
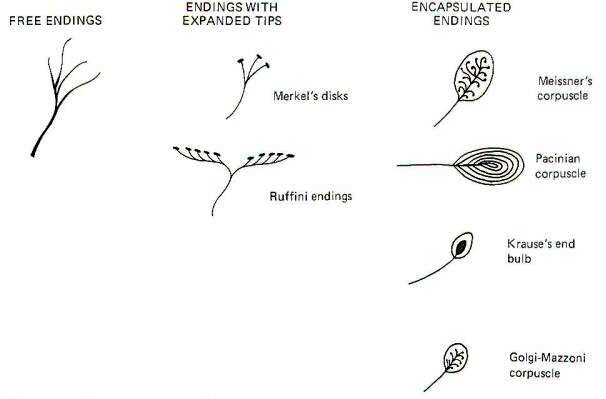
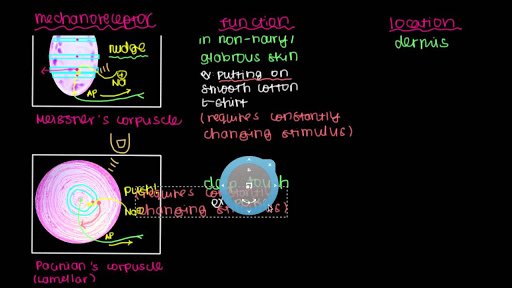
And eventually make its way into this afferent nerve fiber. Articular disk a pad of fibrocartilage or dense fibrous tissue present in some synovial joints. Merkels disks meissners corpuscles ruffini endings and pacinian corpuscles. Merkel cells in the basal epidermis of the skin store serotonin which they release to associated nerve endings in response to pressure.
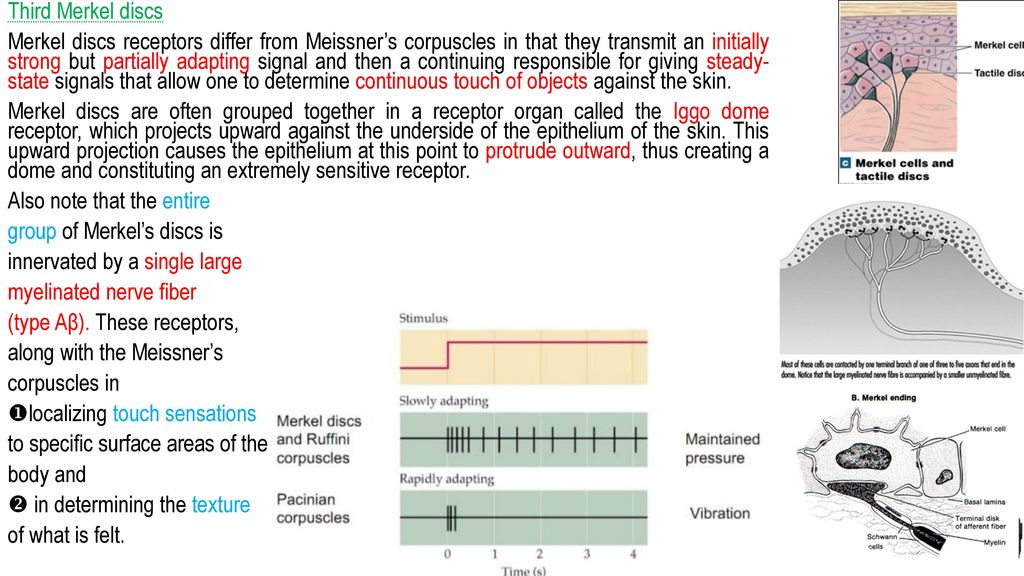
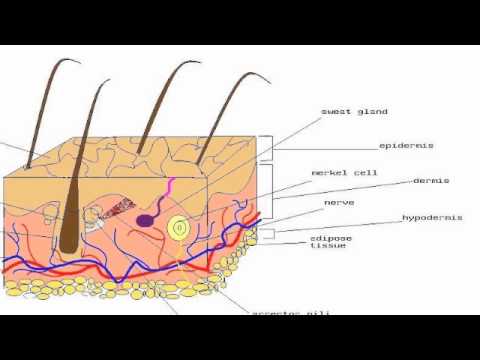
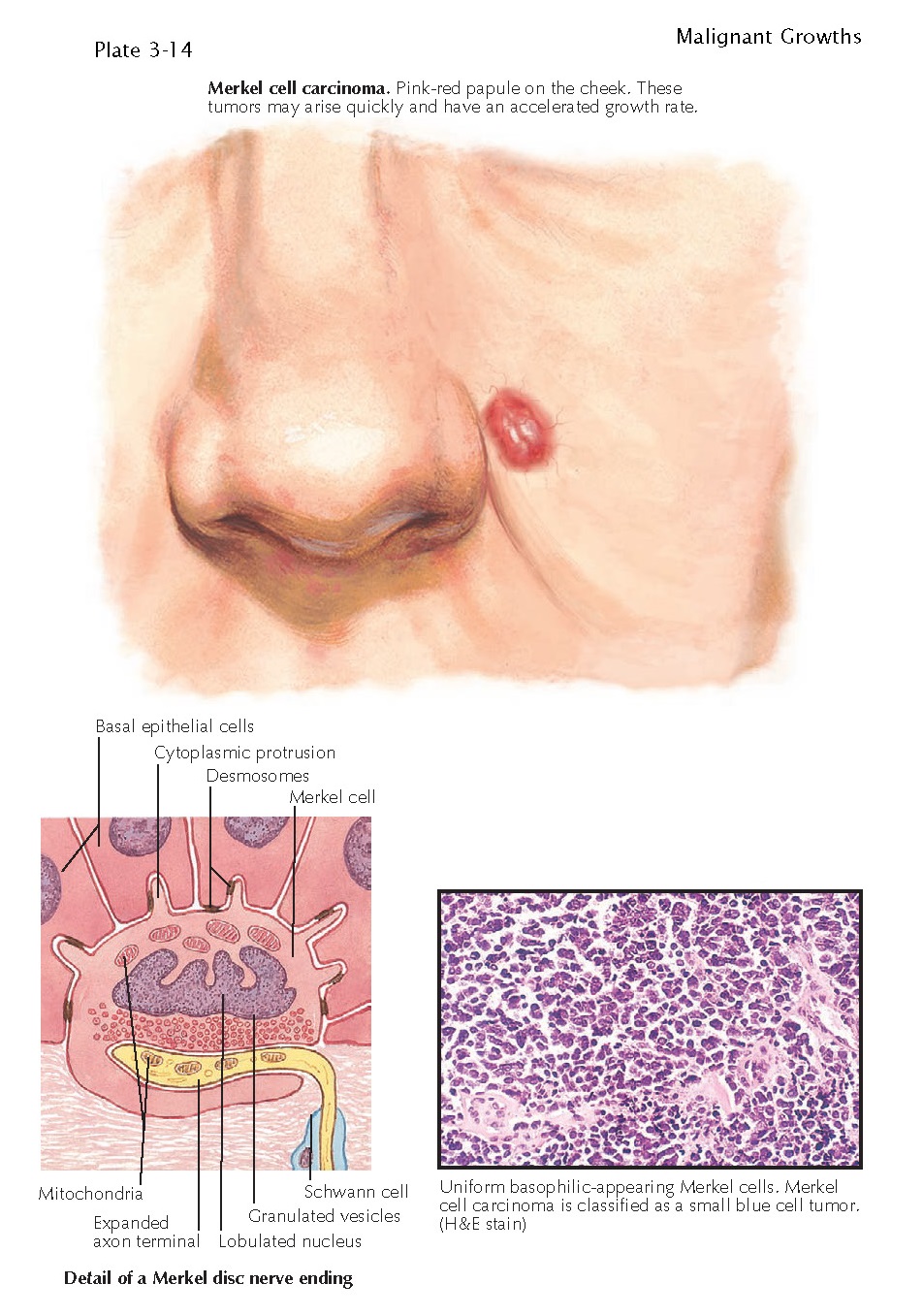
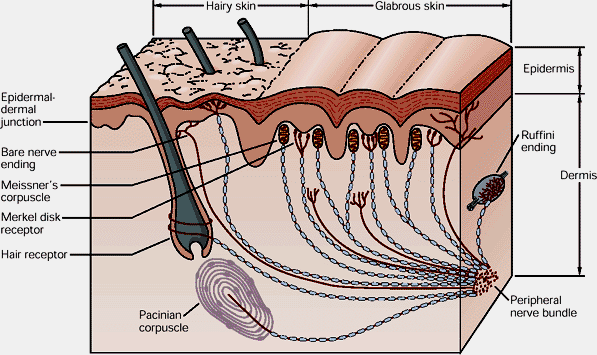
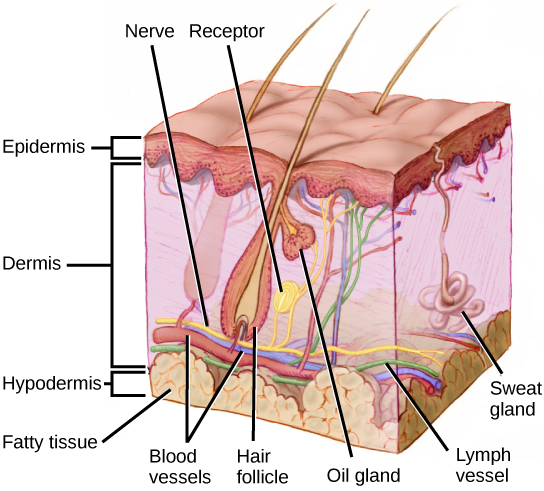
Merkels disks are located superficially in the dermis of skin at the base of the epidermis and lie adjacent to meissners corpuscles and sweat glands. Over 100 years later although not all of the functions of merkel cells are known it is quite clear that they do indeed serve as touch cells and relay touch related information such as texture and pressure to the brain. Disk disk a circular or rounded flat plate. Ciliary disk pars plana.
They are nerve endings and provide information on mechanical pressure position and deep static touch features such as shapes and edges. Merkels disk are slow adapting unencapsulated nerve endings that respond to light touch. Merkel nerve endings are mechanoreceptors a type of sensory receptor that are found in the basal epidermis and hair follicles. These receptors respond to indentation of the skin.
Bowmans disk one of the flat plates making up a striated muscle fiber.


































:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/article/en/peripheral-mechanosensory-receptors/fnl8DI8PJ2YdW6Em8Z2m7g_tf1Nh3joMOYUYb44sj8KBQ_Dendrites.png)